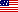
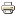
Buildings constructed in 1920-1940-s
Main characteristics. Prefabricated large-panel buildings, mostly frame-panel or frameless (Figure 1, 2):
- 4-5-storied with one-floor panels; and
- 8-storied with two-floor panels.
The building envelope is made of panels (mostly made of reinforced concrete).
Wooden windows.
The roofs are mostly pitched, with a wooden roof frame: hipped or Italian roof.
District heating and hot water supply systems.

Figure 1 – 4-storied panel building

Figure 2 – 8-storied panel building
Energy saving measures. The weakest element of the panel buildings from the viewpoint of heat losses is the building envelope and its low thermal resistance. In addition, there are significant heat energy losses due to the increased infiltration heat exchange caused by loose panel joints. All these weak places create thermal bridges. A very wide-spread example of transmission heat energy losses are losses caused by thermal bridges in places where console façade elements are attached: entrance roof overhangs and balcony slabs. The window structures are usually in unsatisfactory condition, especially in common areas. The situation with the entrance section is similar: the door panels are single and require reconstruction.
Therefore, the recommended measures include:
- Roof insulation (necessarily);
- Heat insulation of the building envelope or insulation of attic floor, combined floor structure or pitched roof with polyurethane foam;
- Insulation of portions of vertical surfaces and constructional wall and roof connections with polyurethane foam (for liquidation of thermal bridges);
- Insulation of the floor or basement floor;
- Heat insulation of basements, foundations and pedestals;
- Replacement of old windows with modern plastic or metal-plastic windows;
- Installation of window ventilators (desirable);
- Heat insulation or replacement of entrance doors;
- Arrangement of a single or double ante-room (if there is space);
- Installation of door closers;
- Installation of reflectors (screens) behind radiators;
- Insulation of pipelines in the heating systems;
- Insulation of pipelines in the hot water supply (HWS) system;
- Installation of manual thermostatic valves on radiators with preliminary adjustment (balancing of the double-pipe heating system);
- Installation of automated heat energy supply unit (individual heat substation (IHS) with weather-based control);
- Reconstruction of the ventilation system with the installation of a heat recuperator (use of central and apartment-level recuperation) (at least, apartment-level recuperation will reduce heat losses and maintain microclimate parameters in the premises after heat insulation of the walls and elimination of excessive infiltration losses);
- Replacement of indoor lighting incandescent lamps (also in common areas) with modern energy efficient lamps;
- Installation of astro timers[1] in the lighting system for common areas;
- Installation of motion sensors in the lighting system for common areas;
- Installation of gas meters. Optimization of work of the building internal gas supply system.
________________________________________________________________________________
[1]Astro timer is a device for precise automatic turn on and turn off for the lighting and other electricity consumers at the time of sunrise and sunset, with daily adjustment during the year. In the process of astro timer setup, GPS coordinates are input, as well as current date and time are set.